In celebration of Women in Construction Week, I thought I’d share my construction journey. People often assume I was born knowing I’d work in construction. When your last name is...

Heat Pump vs Boiler – Which One is Better For You?
By Mike Holmes
Mike’s Advice / Buying & Selling Your Home
Tuesday, June 14th, 2022 @ 10:10am
How to Decide the Best Heating Method For Your Home – Heat Pump vs Boiler?
Choosing the right heating system for your home is a big decision. Heating and cooling account for 63 percent of residential energy use in Canada, according to a Government of Canada publication. Choosing the right system can help you save money on your energy bills. This emphasizes the importance of thoroughly researching all your options before deciding on the best HVAC system for your home, especially with technologies like heat pumps and boilers that present a more advanced and energy-efficient solution for homeowners.
I’m frequently asked what the difference between a heat pump and a heating boiler is, and which is the better choice. Let’s review the two options.
What is a heat pump?
Heat pumps are beneficial as they can heat and cool your home. Heat pumps can use air ducts, radiators, or radiant floors to transmit heat. A zoning scheme is used in the ductless mini-split heat pump.

Mini-Split Heat Pump System Installed In Sunroom in Frank Cozzolino’s Home, in Holmes Family Rescue
Generally, heat pumps work by using power and refrigerant, and there are three types of heat pump systems available today: air-to-air, water source, and geothermal (ground source).
What is a boiler?
A boiler boils water that will heat your home, and the heat is in the form of hot water or steam. However, a boiler can also be a water heater. You can use natural gas, propane, oil, electricity, or pellets (biomass) to fuel the boiler.
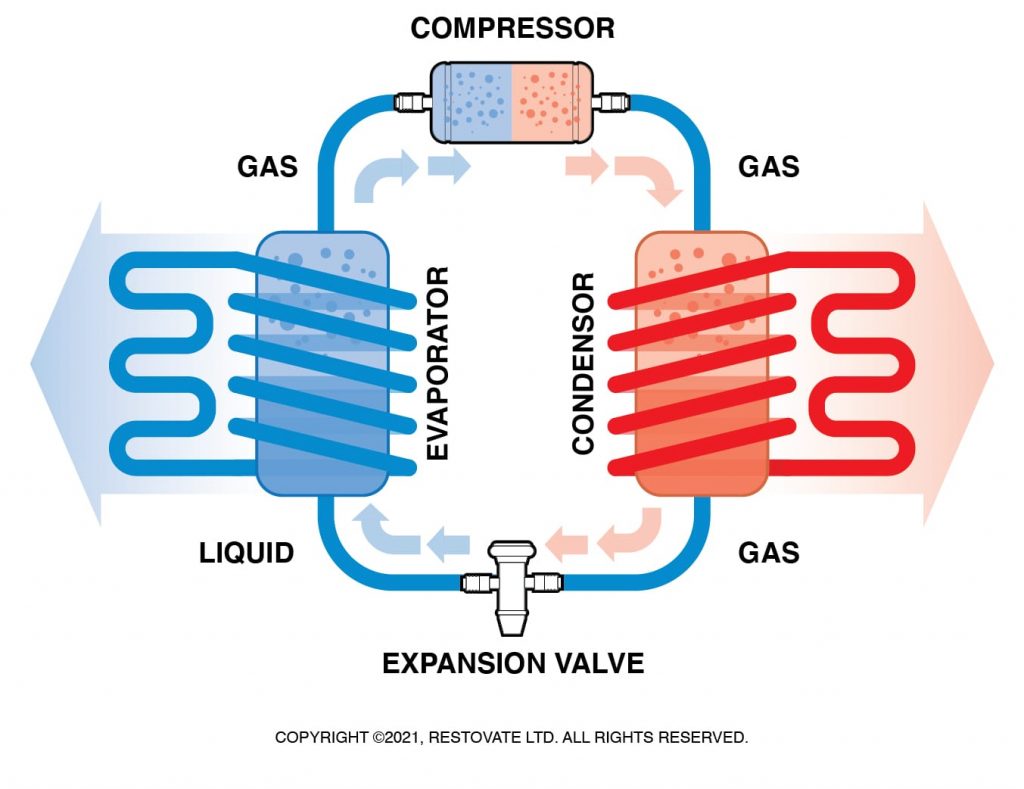
Heat Pumps Explained
How Does a Heat Pump Work?
In its most basic form, a heat pump transfers heat from one site to another using electricity and refrigerant. Think of it as a refrigerator or freezer: it moves heat from inside the box to the outside.
A heat pump provides heat by extracting heat from the air outside your home and transferring it to a refrigeration coolant. The coolant is then compressed, causing its temperature to significantly increase. The coolant is then transferred to the heat pump’s indoor unit, where the air is passed over it via a fan to heat it to your desired home temperature.
In the summer months, your heat pump in cooling mode uses a refrigerant to extract warm air from inside your home and releases it into the air outside.
READ MORE
Main Types of Heat Pump
There are three main types of heat pumps connected by ducts: air-to-air, water source, and geothermal. The most common type of heat pump is an air-source heat pump, and it transfers heat between your home and the outside air.
Compared to electric resistance heating such as furnaces and baseboard heaters, today’s heat pump can save you up to 50% on your heating costs.
Benefits Of A Heat Pump
- Lower operating costs – Heat pumps move heat rather than generate heat. This makes them very energy efficient and can reduce your electricity consumption by 50%
- Less maintenance – annual service checks are recommended with possible tune-ups in the spring and fall
- Ductless systems don’t need any ductwork – this makes them great for small spaces
- Better Safety – Because they rely on electricity rather than burning fuel to generate heat, they pose fewer safety risks than their rivals.
- Lowers Carbon Emissions – lowers your carbon emissions and has an efficient energy conversion rate.
- Some heat pumps are very quiet – with sound levels as low as 20 dBA
- During the summer months, air to air can switch to cooling mode
- Long lifespan – the average lifespan of 14 to 15 years.
- Government discounts are available (please check with your local government and energy boards)
Drawbacks of Heat Pumps
- Higher initial cost – heat pumps have a high upfront cost, but their operational expenses translate to lower long-term energy bills and lower carbon emissions which actually saves you more money down the line.
-
- Always work with a qualified professional contractor to install your heat pump. This is not a DIY job, especially because you are likely dealing with an indoor and outdoor unit.
- Performance issues may arise in extremely cold weather, but a dual fuel backup system may be installed for colder climates
- Planning permissions may be required
Gas Combi Boiler Systems Explained
How Does a Boiler Work?
Condensing boilers are standard on all new boilers. The heat is transferred to the water flowing over the heat exchanger by hot jets connected to it within the boiler. An electric pump then pushes the hot water through your radiators and taps.
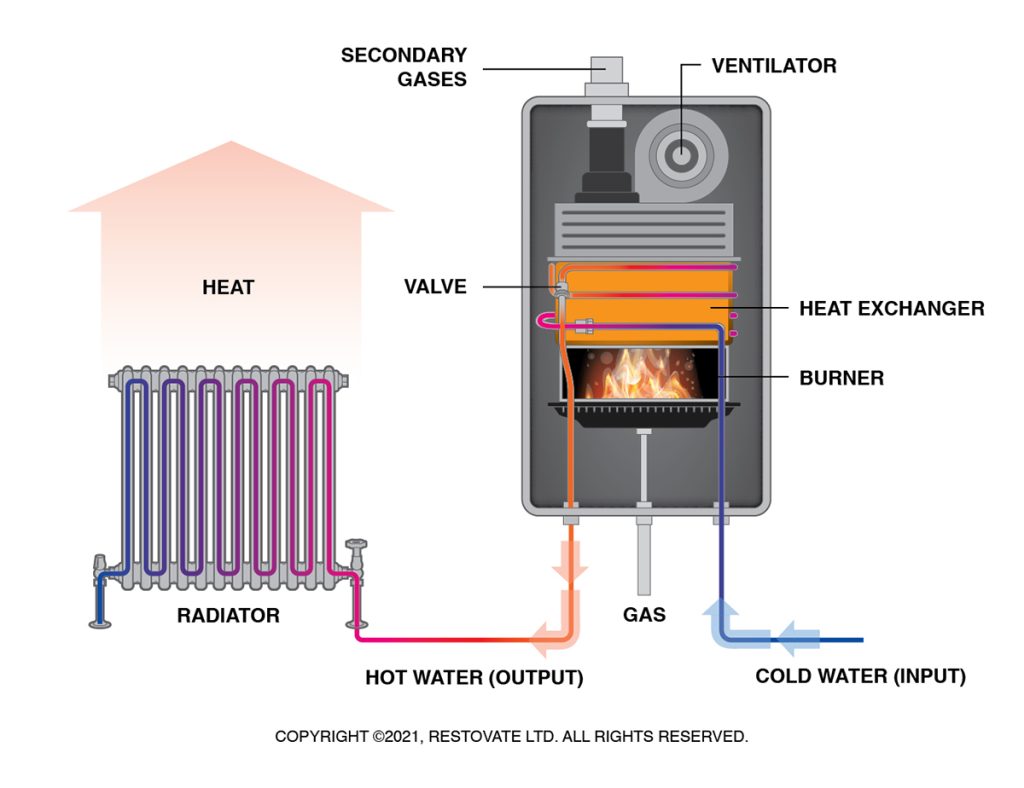
How Do Gas Condensing Combi Boiler Work Illustration
What Are The Main Types of Boilers?
Steam Boiler
A heat exchanger is used in hot water and steam boilers to heat water and send it to a piped system connected to radiators around the house. Steam boilers deliver hot steam to radiators via pressure and gravity, then cycle cooled condensation back into the boiler to be reheated.
Steam heating and hot-water heating are still widespread in many apartment complexes, multi-family houses, and older business buildings. They function well in multi-residence settings and more significant structures.
A pressure relief valve and low water cut-off are required for steam boilers. A manual valve is found on most steam boilers, allowing for the addition of water to the system as needed. Watch out for a “knocking” sound as that may signal a problem with the system.
Hot Water Boiler
Hot Water Boilers provide effective and safe heating to your home’s radiators, by relying on pressure, volume, and temperature. The system circulates warm water throughout your home using one or more pumps.
It’s important to distinguish between hot water boilers and water heaters. Water heaters provide hot water for showers, dishwashers, and tap water. Hot water boilers can heat tap water in a separate tank. However, the water used to heat radiators and the water used to heat tap water must be kept separate.
NOTE: If you already have a heating system in place in your home like a furnace or heat pump and are looking for a water heater, consider tankless water heaters. There are a lot of benefits of going tankless, but one of the biggest benefits is continuous hot water. Here’s a guide on what you need to know about tankless water heaters.
Gas Condensing Boilers
Condensing boilers have two heat exchangers: one to heat the water before it is sent to the radiators and another to reheat water coming from the home’s pipework. It can be fuelled by natural gas pumped through a gas line beneath the house via a conduit from a local municipal source. Another alternative, due to the lack of a natural gas main line in most rural regions, is propane gas from a big tank outside the home.
To reduce fuel use, a temperature gauge and a thermocouple ( a sensor for measuring temperature) are used to manage natural gas. The gas is needed to keep a pilot light lit in the boiler, which warms the heating coils and transfers the heat to the water in the tank. The energy potential in exhaust gases is used to warm the return water to the boiler in condensing boilers. As a result, it has a significantly higher energy efficiency than its non-condensing version
Electric Boilers
Electric boilers heat your home without using fossil fuels such as gas or oil and remain popular due to their high efficiency and environmental friendliness. There are no exhaust gases escaping into the atmosphere, wasting a lot of heat. They don’t require access to the main gas or fuel supply, which is advantageous to rural residents. Electric boilers are less expensive to install, quieter, and take up less space than gas boilers. However, they are not cost-effective in areas where electricity is more expensive than other fuel types.
Oil Boilers
Oil boilers (also known as oil-fired boilers) are oil-fueled water-based heating devices. These are more frequent in rural sections when natural gas is scarce. An oil tank pumps into your oil boiler, which heats the water and sends hot air or water through your home’s plumbing. Older oil boilers can be inefficient in terms of energy use. Your oil boiler is usually not very environmentally friendly if it has a natural draught, a continuous pilot light, or a large heat exchanger. While retrofitting is an option, you should consider completely replacing the unit.
READ MORE
What is a Combi Boiler?
Most boilers that do heat your home and your water, are often referred to as combi boilers. Unlike a traditional boiler, a combi boiler may produce hot water on demand rather than keeping it in a tank or cylinder. This hot water can heat your home and run your appliances and faucets. Because it is a single machine that provides two ‘combined’ functions: heating and hot water, it is called a combi boiler.
Benefits of A Combi Boiler
Due to their small size, high efficiency of 95 percent, and capacity to accomplish two tasks at once, condensing combi (or combination) boilers are becoming increasingly popular. They provide hot water directly to your kitchen and bath, eliminating the need for a storage tank, while still maintaining a primary hydronic loop to heat the home utilizing radiators or other heat-emitting equipment. This also makes them great for smaller homes and spaces because a cold-water feed tank or a hot water storage tank is not required.
Heat Pump and Boiler Comparison
Both heat pumps and combi boilers are great options for heating and cooling your home. Each one has different features that will depend on your needs and your home’s needs. Let’s compare them on efficiency, installation, lifespan, maintenance, user experience, eco-friendliness, space needed, and noise.
Heat Pump vs. Boiler – Efficiency
Modern heating boilers that are well-maintained can offer up to 98.5 percent AFUE (energy efficiency) but heat pumps are even more energy-efficient. Modern heat pumps can reach up to 400 percent efficiency by recycling heat energy from the air, water, or ground.
Look for brand models that are compact, highly efficient, gas condensing boilers, and insulated for ultra-quiet performance. Som offer 95% AFUE and come in compact wall-hung and floor-standing designs.
Heat Pump vs. Boiler – Installation
Typically, a heating boiler system is relatively easy to install. There are two exceptions, however. One is if you need to install a distribution system or retrofit/repair your existing distribution system. The other is if you need an external hot water storage tank to supply hot water to your home, if you’ve bought a heat-only boiler.
An air-to-air heat pump that is ducted or ductless is also relatively easy to install.
Heat Pump vs. Boiler – Lifespan
A heat pump can last twice as long as a boiler. While there is a significant investment upfront, it will last a very long time. The heat pump can go on heating a home for over 20 years, closer to 30 if well maintained. (50 up above) Modern boilers on the other hand need replacing every ten years, 15 years at a push.
Heat Pump vs. Boiler – Maintenance
You should schedule heat pump or boiler maintenance with an HVAC professional at least once a year. However, ideally, a heat pump should be tuned up twice a year in the spring and fall to maintain appropriate performance and energy efficiency.
Heat Pump vs. Boiler – User Experience
Working with gas is a complex and dangerous task that requires extensive training, knowledge, and experience. It’s a good idea to get your boiler system tested by a licensed residential boiler repair professional at least once a year. A qualified expert can perform the necessary tests and adjustments to ensure that your boiler runs smoothly and safely.
Heat Pump vs. Boiler – Eco-Friendliness
Geothermal heating, according to Energy Star reports, is the most environmentally friendly and efficient way to heat your home. This does, however, necessitate an initial investment in a geothermal heating system.
Another great option is condensing boilers. Residential condensing boiler systems provide a comfortable heating solution as well as providing domestic hot water. They can be highly efficient and reliable. Plus, new models offer whisper-quiet operation that is great for radiant heating applications such as panel radiators, in-floor radiant heating, and baseboards.
An air-to-air heat pump uses integrated sound-dampening features to keep noise to a minimum, making it one of the quietest air-to-air systems on the market.
Heat Pump vs. Boiler – Space Needed
When installing, consider the size of the unit, the safety zone, and the manufacturer’s instructions. A heating boiler is installed indoors and can be mounted on the floor or the wall. If you want your heating boiler to also provide hot water, you have two choices: a traditional hot water tank or a smaller combi-boiler that connects to the water mains and eliminates the need for a tank.
A heat pump requires both indoor and outdoor space. The amount of outside space needed varies depending on the type of heat pump. Indoor units are typically small and can be placed higher on the wall to save space. An air-to-air heat pump takes up about the same space as a standard outdoor air conditioner.

Heat Pump Outdoor Unit Installed on one of our latest projects for Holmes Family Rescue.
Heat Pump vs. Boiler – Noise
All heating systems make some noise. However, heat pumps are usually quieter than fossil fuel boilers. A ground source heat pump’s noise level can reach 42 decibels, whereas an air source heat pump’s noise level can range from 40 to 60 dB, depending on the brand and installation.
A heat pump’s indoor and exterior components both create noise. Most modern heat pump outdoor systems have a sound level of roughly 60 dB, which is about the same as light rain or a regular conversation. When installing a heat pump, you must consider the location, so the noise does not disrupt your lifestyle. Installing them beneath bedroom windows or other windows in areas where quiet time is desired is not advised.
What to Consider When Buying Heat Pump or Boiler?
Before you purchase a new heat pump, you must ensure the rest of your home is as energy-efficient as possible. This will allow you to buy a smaller, less expensive system.
Tips to help you make your home more energy-efficient:
- Add insulation to your attic and exposed walls
- Add weather stripping around doors and windows, and ensure caulking is not old and cracking
- Ensure your ductwork is properly sealed throughout your home
- Insulating ducts in crawlspaces and attics
- Installing a programmable thermostat
What Features To Consider When Buying A Boiler vs. Heat Pump?
Boilers:
- Efficient and save energy
- Durable and long-lasting
- Low maintenance and repairs (with annual inspections and servicing)
- Provide even distribution of heat
Heat Pumps:
- Efficient and save energy (use less energy and fuel to heat/cool home)
- Durable and long-lasting (lifespans from 30 to 50 years with proper maintenance)
- They provide warm and cold air and an even distribution
- Improve indoor air quality by filtering and dehumidifying the air
- It runs by electricity and thus reduces emissions
- Low maintenance and repairs (with annual inspections and servicing)
Heat Pump vs. Boiler Warranty
Typically, the heat pumps manufacturer’s warranty is five years. However, some companies provide a ten-year manufacturing warranty for their product. To me when a company can offer this type of warranty, you know they stand behind their products and can Make It Right for your home!
Most boilers come with a standard 1-year warranty, while other warranties are extended two to ten years.
Heat Pump vs Boiler – Which One Is Better for Your Home?
Heat pumps are often an excellent solution for households without access to gas mains and are preferable to an oil boiler, which emits a lot of carbon dioxide (CO2). However, heat pumps are not as well suited to providing large heat boosts as gas-fired boilers. However, consulting with a licensed heating and cooling professional is your best bet as they will assess your home and current systems and make suggestions for a solution that is right for you!
READ NEXT
FAQ’s
Is a heat pump more efficient than a boiler?
By recycling heat energy from the air, water, or earth, modern heat pumps may achieve up to 400 percent efficiency.
Can a heat pump replace a boiler?
Yes, in many circumstances, a heat pump may provide all of your home’s heating and hot water needs and can replace traditional gas boilers, which eliminates the need for additional costly retrofitting after the heat pump is installed.
When should you use a boiler vs. a heat pump?
If you rely on radiators, coils, and radiant floors to heat your home then you will require a boiler. On the other hand, a heat pump can only effectively chill your property if you use air duct distribution.
Are heat pumps as good as a gas boiler?
Modern heating boilers can provide up to 98.5 percent AFUE (energy efficiency). But the heat pump blows away even this near-perfect rating. Because heat pumps recycle heat energy from the air, water, or ground, a modern heat pump can achieve up to 400 percent efficiency.
Heat pumps are now widely regarded as one of the most energy-efficient heating systems available. Heat pumps are typically a good alternative for houses without access to mains gas and are preferable to an oil boiler, which emits a lot of carbon dioxide (CO2). However, once temperatures drop below freezing, the most popular heat pump, the air-source version, loses its ability to heat an indoor room adequately.
Are heat pumps worth the money?
Heat pumps are a good alternative for new homes and retrofits of existing heating and cooling systems in various situations. They’re also a viable alternative for replacing old air conditioning systems, as the cost difference between a cooling-only system and a heat pump is frequently negligible. We recently got a heat pump installed on one of our projects for Holmes Family Rescue, to provide heating/cooling for a solarium that we built. I have to say, it’s great! It’s quiet and doesn’t require a lot of space and is energy efficient!
What problems can come up with heat pumps?
If your heat pump isn’t cooling, it’s most likely due to a dirty coil or fan. See if cleaning them up makes a difference. Also, check that the air duct or the air handler are not blocked. If yes, clear them out. If any of the pump’s auxiliary heating elements are damaged, you can replace them.
Can a heat pump heat a whole house?
A whole-house heat pump can heat and cool your entire home, making it an excellent option for people looking for a cost-effective solution.
At what temperature do heat pumps become ineffective?
Air source heat pumps can operate in temperatures as low as -10 degrees Fahrenheit! If you’re concerned—or live in an area with frigid temperatures, you can acquire a heat pump with an emergency supplemental heating system, but most people never need it.
Should I replace my boiler with a heat pump?
It depends on your needs. A heat pump may provide all of your home’s heating. However, if you’re looking for a system that heats your home and your water effectively, I recommend checking out condensing boilers.
Are heat pumps a greener alternative?
The benefits of heat pumps clearly show that they are a wise long-term investment. Heat pumps are worth it, given that the operating costs save you money on your energy bills because the mechanism moves heat from one place to another rather than producing it, and government rebates aid you in your transition to a green energy solution.
With that in mind, the use of various heat pumps as a low-carbon heating solution will likely continue to grow. You may be concerned about the significant upfront costs, but you must look at the big picture, and solar panels with heat pumps equal a path to net-zero energy.