Dream of a career where your skills bring joy, enable freedom, and create unforgettable memories? The thriving recreational vehicle (RV) industry offers just that! It’s more than fixing vehicles; it’s...

7 FAQs about Radon and Radon Mitigation System DIY
By Mike Holmes
Mike’s Advice / Home Safety & Maintenance
Monday, February 3rd, 2020 @ 12:00pm
I’ve been talking about radon for a few years now and I love when homeowners reach out with questions about it. It’s important to pay attention to your indoor air quality, especially if you have kids and pets living in your house. I am going to answer some of the questions I am frequently asked about radon in this article.
What Is Radon Test?
What is Radon? For those of you who don’t know, radon is the leading cause of lung cancer for non-smokers. Uranium is everywhere in the ground and in all kinds of soil, and when it starts to break down it creates a radioactive gas that is odorless, colorless, and tasteless. This gas is radon. Here is more information on how radon enters your home.
The radon test is a test to identify the level of radon in your home. A radon test can be done by a professional home inspector or by yourself using a radon test kit or the radon tester. Testing radon can be a DIY project. Besides, there is also radon testing equipment for inspectors.
7) Do houses on a slab need to be concerned about radon?
Radon gas can migrate through plastic and concrete, so the answer is yes. Radon enters anywhere it finds an airway where the house contacts the soil. This includes cracks in foundation walls and floor slabs, construction joints, gaps around service pipes, support posts, window casements, floor drains, and sumps. If your vapour barrier membrane isn’t durable enough, it can tear during construction, and radon will come in that way as well.
Radon In The House
Radon concentration levels will vary from one house to another, even in the same neighborhood. The only way to be sure of the radon level in your home is to test. The air pressure inside your home is usually lower than in the soil around your foundation. This pressure difference draws air and other gases, including radon, from the soil into your home. Radon can enter the house through:
- Soil
- Windows
- Cracks in walls & floors
- Loose pipe fittings & support posts
- Floor drains & sump pumps
- Wall & floor joints
- Ground water
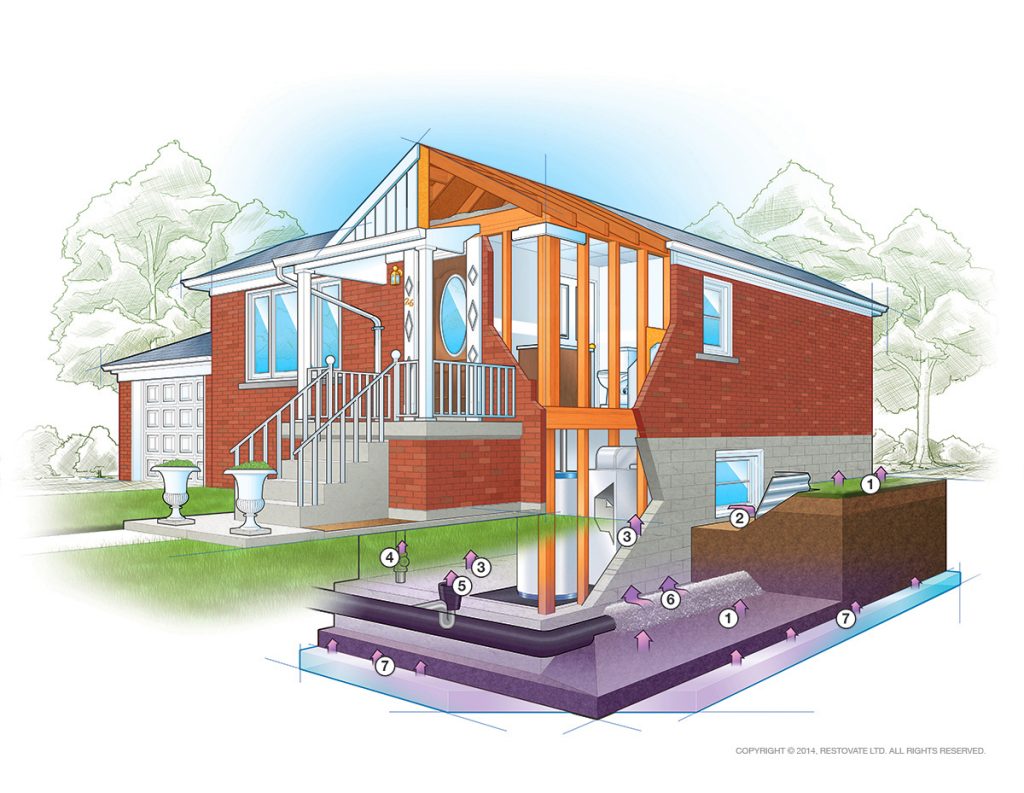
Radon can seep into a home through pipes, windows, sumps, unfinished floors, cracks in foundation walls and floors-even through foundation walls.
6) Should I Buy a DIY Radon Test Kit?
The easiest way to purchase a radon test kit is online. You can also find them in some local hardware stores. Most testing kits will cost you under $50.

Remember that you will have to send your test results to a lab. Turnaround time for the lab results is usually 10 days.
You can also hire a professional to do the radon test for you. Make sure the person you hire is certified by the Canadian National Radon Proficiency Program (C-NRPP).
My Mike Holmes home Inspectors are fully trained professionals, certified by the Canadian National Radon Proficiency Program (Canadian-NRPP). Mike Holmes Inspections is also a recognized certified C-NRPP lab where we do our own in-house analysis in order that you can receive your results quicker. You can book a Mike Holmes inspection here.
RELATED: How To Remove Radon From Your Well Water
5) Where Does Radon Come From?
Radon is a radioactive gas that comes from the breakdown of uranium in soils, rock, and water. In enclosed spaces like residential and commercial properties, it can accumulate to dangerously high levels. Radon is the 2nd leading cause of lung cancer after smoking. It’s a colorless, odorless gas so the only way to know how much is in your home is through testing.

Radon gas can enter your home through any opening where the house is connected to the ground. This includes cracks in your foundation, floor drains, and even your well water.
4) What’s the difference between a short-term and a long-term radon test?
Short-term radon tests take less than 30 days but should be followed up a long-term radon test which takes several months. The short-term tests should be used for initial screening only. According to Health Canada, you should be tested for at least 3 months. Radon levels can fluctuate over time (even hourly), so a long-term test is a more accurate test to know the radon level in your home. You can purchase radon tests here.
Short Term Radon Test
Short-term radon tests usually take between 2-30 days. They are considered a screening test. This should be followed up with a longer-term test of 90-365 days. If you are going away on vacation, it might be a good time to test for radon since you won’t be opening your doors or windows.
Even a 48 to 96 hours test is a good first step towards radon detection in your house. You can purchase do-it-yourself radon test kits but I think its best to hire a radon measurement professional.
Long Term Radon Test
A long-term radon test will give you a more accurate indication of your average annual radon concentration and exposure risk than a short-term test. Health Canada recommends testing for a minimum of 3 months. You should know that radon levels in homes can fluctuate day by day. We’ve seen levels change by as much as 2-3 times in 24 hours.
We also see variations between seasons, and that can be even larger.
3) How often should I re-test my home for radon gas?
We recommend testing your home for radon every 2-3 years. It’s not necessary to retest your home every year. It costs about $40-50 to do the radon test yourself, or about $200 if you hire a radon expert.
2) How is radon measured?
Radon is measured in units of picocuries per liter (pCi/L) in the US or becquerels per cubic meter (Bq/m3) in Canada. I actually heard from a homeowner in Ottawa whose home was tested for radon. His radon levels? 1,600 Bq/m3.
25,000 deaths in North America every year can be attributed to radon gas. Get your home tested for radon.
The radon guideline set by Health Canada is 200 Bq/m3. It’s lower in the US, where the EPA action level is about 150 Bq/m3 (or 4.0 pCi/L), and the World Health Organization level is the lowest at 100 Bq/m3. The WHO states that there is no level below which radon can be considered safe. If a home is testing above these levels, you need to take action. And don’t worry, there are fixes!
1) How much does it cost to get rid of radon?
Generally, the cost for mitigating against radon is between $1,500 and $3,000. When you think about how much you spend on upgrading your finishes and making aesthetic changes to your rooms, mitigating your home against this very dangerous gas does not cost that much.
RELATED: HOW TO GET RID OF RADON (IN 100 DAYS OR LESS)
READ NEXT:
- RADON TEST OPTIONS
- BUILDING A NEW HOME? HAVE YOU CONSIDERED RADON TESTING?








